“What is Resistance to Sulfuric Acid and Hydrochloric Acid Dew Point Corrosion? ~An Explanation!! vol.2~”
- Product
- S-TEN

※)Please note that the contents of this article reflect our own views and are not a guarantee of all aspects. When purchasing or processing products, please confirm with specialized companies, including ours, and conduct verification according to the intended purpose and usage before using the materials in question.
In vol.1, we introduced the overview of S-TEN®, sulfuric acid dew point corrosion, hydrochloric acid dew point corrosion, as well as points of caution regarding S-TEN® applications and operations. This time, we will explain the following topics.
Contents of vol.2
・Specifications of S-TEN®
・Distinctions between S-TEN1® and S-TEN2®
・Welding and processing of S-TEN®
・Application examples
Specifications of S-TEN® steel
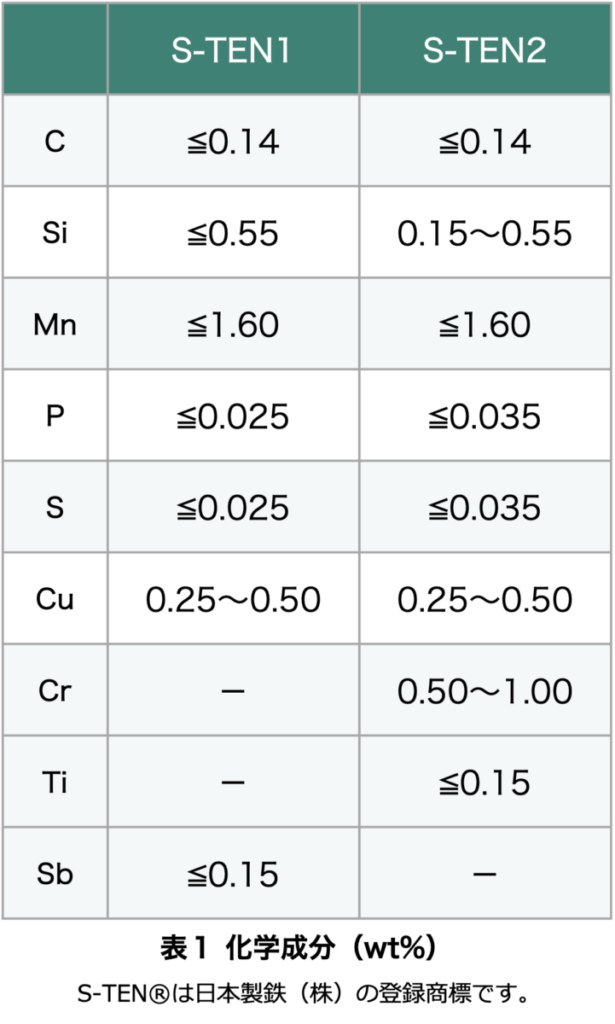
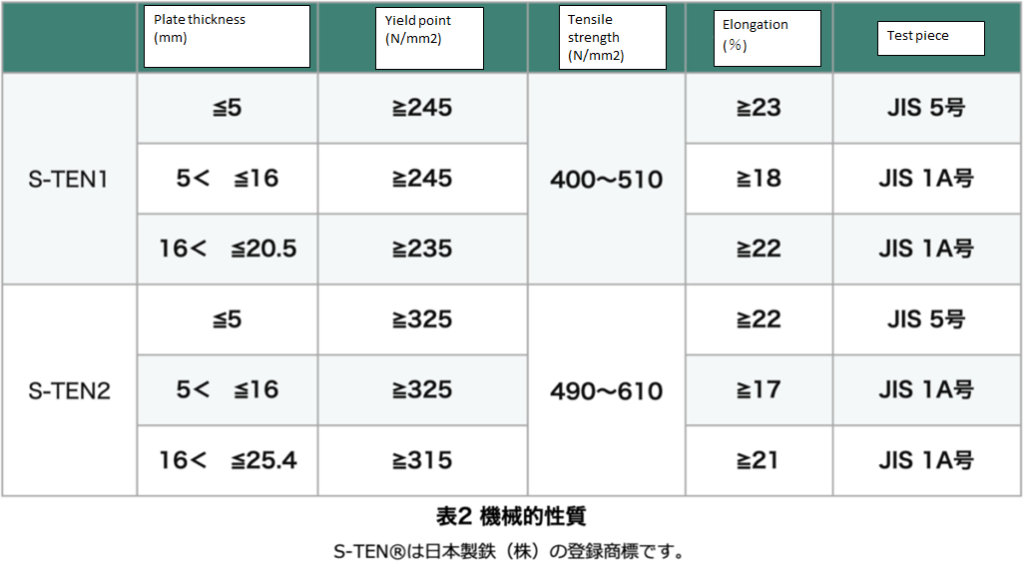
S-TEN® has two types: S-TEN1® and S-TEN2®. These are not public standards but are specifications set by Nippon Steel. The specified values for thick plates are shown in Tables 1 and 2.
The chemical composition is mainly determined to provide corrosion resistance.
Regarding mechanical properties, S-TEN® is designed to meet the standards of SM400A in JIS G3106, which is a rule established to unify the quality and safety of products and services in Japan nationwide. Similarly, S-TEN2® is designed to meet the standards of SM490A in JIS G3106.
Therefore, it can be applied to public works requiring JIS-certified materials or uses such as chimneys subject to the Building Standards Act. However, to have the steel material inspection certificate (mill sheet) indicate that it is JIS-compliant material, it is necessary to specify this before placing the order.
By doing this, surplus S-TEN® can be used as SM material. Of course, the reverse is not possible. Although the mechanical properties differ, in addition to thick plates, there are also hot-rolled materials, cold-rolled materials, and steel pipes available, so please feel free to consult with us.
Differentiation between S-TEN1® and S-TEN2®
The primary difference in the usage of S-TEN1® and S-TEN2® lies in whether the environment involves hydrochloric acid dew point corrosion.
In cases where hydrochloric acid dew point corrosion or hydrochloric acid pickling tanks are involved, S-TEN® is the standard choice.
“The catalog recommends S-TEN2® for high-temperature exhaust gas in the range of 350–500°C. This may be due to the original design concept, as S-TEN2® was aimed at high-temperature and high-concentration applications. However, since there is not a significant difference between the two, either should suffice. In terms of absolute high-temperature strength, S-TEN2®, with its higher base material strength, performs better. Additionally, S-TEN2® also has higher strength at room temperature, making it the preferred choice when high strength is required in the design.
S-TEN2® has better weather resistance, so it may be preferable for outdoor facilities exposed to the atmosphere. In any case, accurate judgment would likely require evaluation in the actual environment.
Welding and processing of S-TEN®
As can be seen from the fact that S-TEN® can also substitute for SM materials, its weldability is excellent.While alloy elements are added, the carbon and manganese content are reduced accordingly, resulting in equivalent weldability.
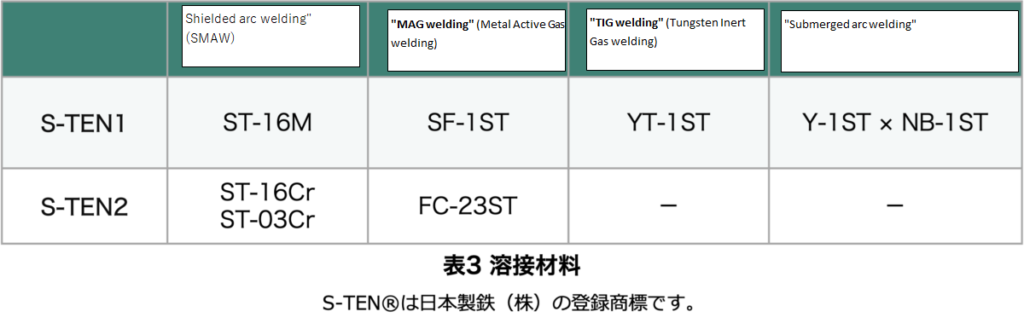
However, since the welded sections must possess the same resistance to sulfuric acid dew point corrosion and hydrochloric acid dew point corrosion as the base material, specialized welding materials, as shown in Table 3, considering the composition of the base material, are required when welding S-TEN® steel together.
The Nippon Steel catalog features photographs showing that when specialized welding materials are used, the welded sections exhibit the same corrosion resistance as the base material. For welding between S-TEN® and stainless steel, dissimilar joint welding materials are required.
“For welding between S-TEN® and general steel, corrosion resistance is not likely to be required for the welded sections, so standard welding materials should suffice in such cases.
Cutting, bending, and other processing of S-TEN® are also possible in the same way as SM400A and SM490A, without requiring any special considerations. In this sense, it can be said to be an easy-to-handle material.
Application examples
More than 50 years have passed since the launch of S-TEN®, and it has maintained overwhelming market competitiveness over the years.
A large number of facilities have applied S-TEN®.
“Thermal power plants, waste incineration facilities, electric furnace factories, paper mills, cement plants, ships, petroleum refineries, plating factories, and so on. In terms of equipment, flues, chimneys, dust collectors, air preheaters, heat exchangers, economizers, flue gas desulfurization devices, hydrochloric acid pickling tanks, and so on.”
Where there is combustion, there is S-TEN®. Please feel free to consult us, including for new applications.
We are a specialized trading company based in Japan, dealing in high-tensile steel and other special steels.
Please feel free to contact us.
Feel free to email us.
↓↓↓
info@kumagai-steel.co.jp

